
Potatoes, a staple in many diets worldwide, have long been celebrated for their versatility and nutritional content. From mashed potatoes to french fries, this humble tuber has found its way into countless recipes. However, beneath its starchy exterior lie certain disadvantages that warrant consideration. In this exploration, we delve into the less-appreciated aspects of potatoes, shedding light on their potential drawbacks and urging a more balanced perspective on their consumption.
- High Glycemic Index and Blood Sugar Concerns:
One significant disadvantage of potatoes is their high glycemic index (GI), a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Potatoes, especially when consumed in processed forms like potato chips or fries, can lead to rapid spikes in blood glucose. This poses a concern for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage their blood sugar levels. Consistent consumption of high-GI foods may contribute to insulin resistance over time, potentially increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
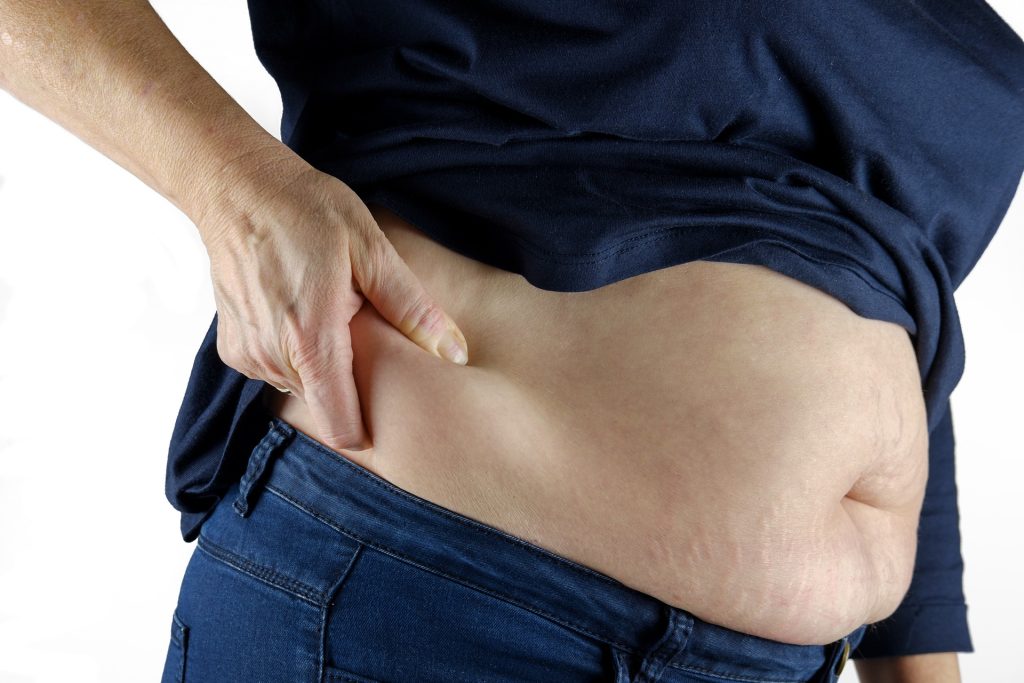

- Weight Management Challenges:
Potatoes are calorie-dense and can be a double-edged sword for those struggling with weight management. While they offer satiety due to their high fiber content, how they are prepared can significantly impact their caloric load. Excessive calorie intake is contributed by fried and processed potato products, laden with unhealthy fats and additives. Overconsumption of such high-calorie potato dishes may lead to weight gain, posing a challenge for individuals aiming to maintain or lose weight.
- Nutrient Imbalance:
While potatoes are a good source of certain essential nutrients, they are not nutritionally complete. Relying heavily on potatoes as a dietary staple may lead to nutrient imbalances, as they lack some crucial vitamins and minerals. A diet predominantly centered around potatoes may result in deficiencies in nutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin B12, and calcium. To mitigate this, incorporating a variety of foods to ensure a well-rounded and nutritionally adequate diet is essential.
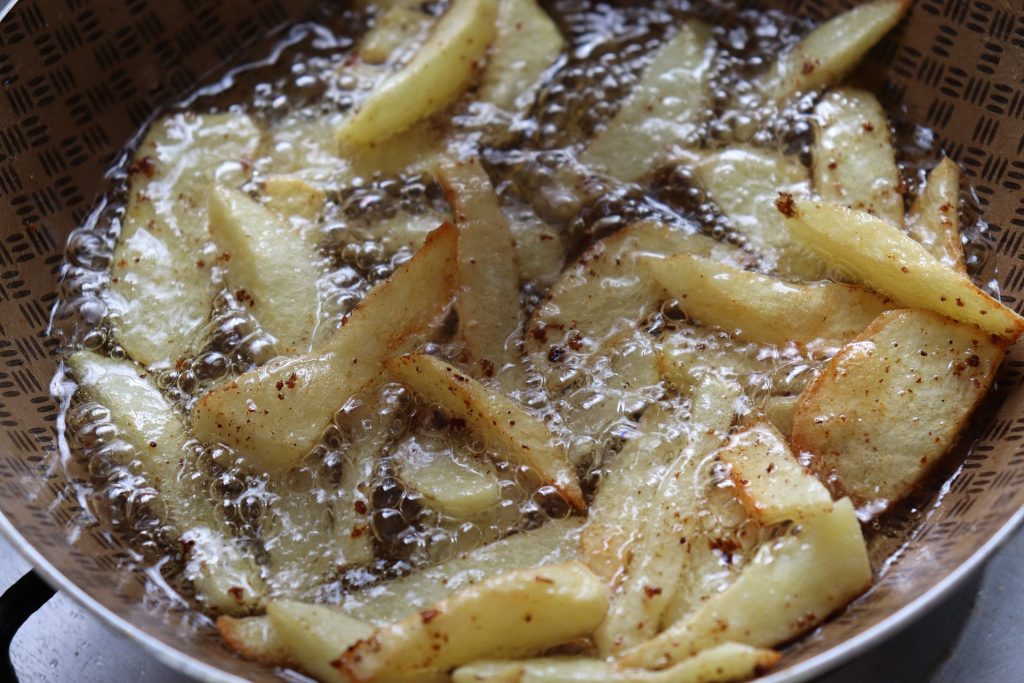

- Acrylamide Formation during Cooking:
Cooking potatoes at high temperatures, especially through methods like frying or baking, can undergo a chemical reaction that forms acrylamide. This substance has been identified as a potential carcinogen in animal studies, raising concerns about its impact on human health. While the levels of acrylamide in cooked potatoes are generally considered safe, it highlights the importance of moderation and choosing healthier cooking methods to minimize potential risks.
- Allergies and Sensitivities:
Potatoes belong to the nightshade family, and some individuals may experience allergies or sensitivities to these vegetables. Symptoms can range from mild digestive discomfort to more severe allergic reactions. It is crucial for individuals with known sensitivities or allergies to nightshades to exercise caution and be mindful of their potato consumption. Exploring alternative starch sources may be necessary for those who need to avoid potatoes due to allergic reactions.
Conclusion:
While potatoes undeniably contribute to the culinary landscape with their versatility and nutritional benefits, it is essential to acknowledge their potential disadvantages. From concerns related to blood sugar management and weight control to the formation of acrylamide during cooking, understanding the drawbacks allows for informed dietary choices. Moderation and a diverse, balanced diet are key to reaping the benefits of potatoes while mitigating their potential adverse effects. By fostering awareness of these disadvantages, individuals can make more informed decisions about the role of potatoes in their overall nutrition and well-being.







